A Comprehensive HRIG Solution
HyperRAB (300 IU/mL) is the first and only high-potency human rabies immune globulin (HRIG) that enables the delivery of more of the total dose per mL at the wound site, no matter the wound size or patient weight.1-3
(rabies immune globulin [human])
A comprehensive HRIG solution designed with patients, healthcare teams, and institutions in mind.

HyperRAB (300 IU/mL) is the first and only high-potency human rabies immune globulin (HRIG) that enables the delivery of more of the total dose per mL at the wound site, no matter the wound size or patient weight.1-3
*Store HyperRAB at 2 to 8°C (36 to 46°F). Do not freeze. Store at room temperatures not to exceed 25°C (77°F) for up to 6 months at any time prior to the expiration date, after which the product must be used or discarded.

4000+
The number of healthcare professionals who have participated in 100+ live Grifols-sponsored educational sessions on rabies postexposure prophylaxis⁴*
* Numbers reflect data collected since 2015

2500+
The number of unique emergency room facilities visited by a Grifols rep with 200+ educational sessions conducted on site at hospitals across the country4*
* Numbers reflect data collected since 2015

A history of innovation
Grifols pioneered many of the sophisticated techniques used in the industry today to collect, test and manufacture plasma-derived medicines.
A leader in plasma collection
Grifols has more than 300 plasma donation centers that provide dependable supply needed to reproduce essential plasma-derived therapies
HyperRAB is an HRIG that provides rapid immune coverage, indicated for postexposure prophylaxis (PEP), along with rabies vaccine, for all persons suspected of exposure to rabies.1,6 Review the CDC guidelines for PEP.
For unvaccinated persons, the combination of HyperRAB and vaccine is recommended for both bite and nonbite exposures regardless of the time interval between exposure and initiation of PEP. Persons who have been previously immunized with rabies vaccine and have a confirmed adequate rabies antibody titer should receive only vaccine.1
Grifols is the only manufacturer that has complete end-to-end control over the entire process—collection, testing, fractionation, and supply—enabling a consistent and reliable supply of HyperRAB.4,5
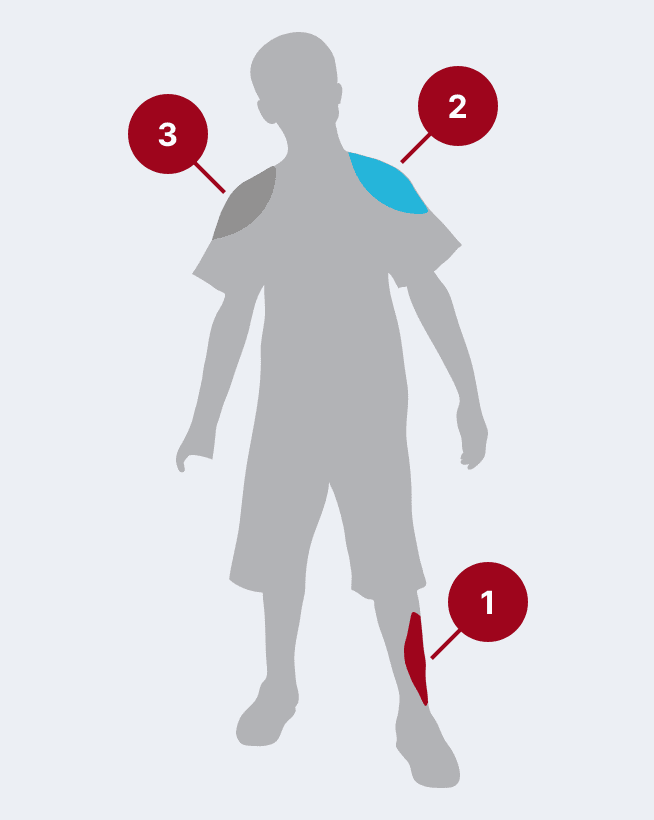
The recommended dose for HyperRAB is 20 IU/kg (0.0665 mL/kg) of actual body weight administered at the time of the first vaccine dose.1 HyperRAB can be given up to 7 days after the first dose of rabies vaccine.
Administer as much of the dose of HRIG as possible directly into or around the wound where the highest viral load occurs.
HRIG should never be administered in the same syringe or needle or in the same anatomical site as the first vaccine dose.
Any remaining volume (or if there is no wound) should be injected intramuscularly (IM) at a site distant from vaccine administration. The CDC recommends that the full dose always be administered.
The vaccine should be injected in the deltoid area opposite of the HRIG injection or wound. Do not inject rabies vaccine or HRIG in the gluteal area due to risk of diminished immunologic response and injury to the sciatic nerve; however, HRIG may be infiltrated in the gluteal area if that is an exposure site.
The most common causes of postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) management failures are when the HRIG is not fully administered, it is not administered into the wound(s) and injected only IM, or injections are not administered to all bite wound(s).12,13 ‡
‡ If the HyperRAB dose has insufficient volume to infiltrate the entire wound, the HyperRAB dose may be easily diluted with an equal volume of dextrose 5% in water (DSW).1

Store safely at room temperature
Up to 6 months*

Longest shelf life available among HRIG products4,5
3 years—may decrease some concerns around unused and expiring product
*Store HyperRAB at 2 to 8℃ (36 to 46℉). Do not freeze. Store at room temperatures not to exceed 25℃ (77℉) for up to 6 months at any time prior to the expiration date, after which the product must be used or discarded. Do not return to refrigeration.1
In an open-label, single-arm study of 12 healthy volunteers, rabies virus antibody titers were assessed following a single 20 IU/kg IM injection of HyperRAB. This was measured by a rapid fluorescent focus inhibition test (RFFIT).14
HyperRAB (rabies immune globulin [human]) 300 IU/mL produced a substantial increase in antirabies virus antibody concentrations during a 21-day period in which peak values were achieved.1,14
In the clinical study, subjects underwent a screening period of up to 21 days, when safety assessments and laboratory tests were performed to ascertain eligibility. A single IM dose of HyperRAB was administered to eligible subjects on day 0, followed by repeated measurements of rabies virus antibody concentrations on days 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 14, 18, and 21.14
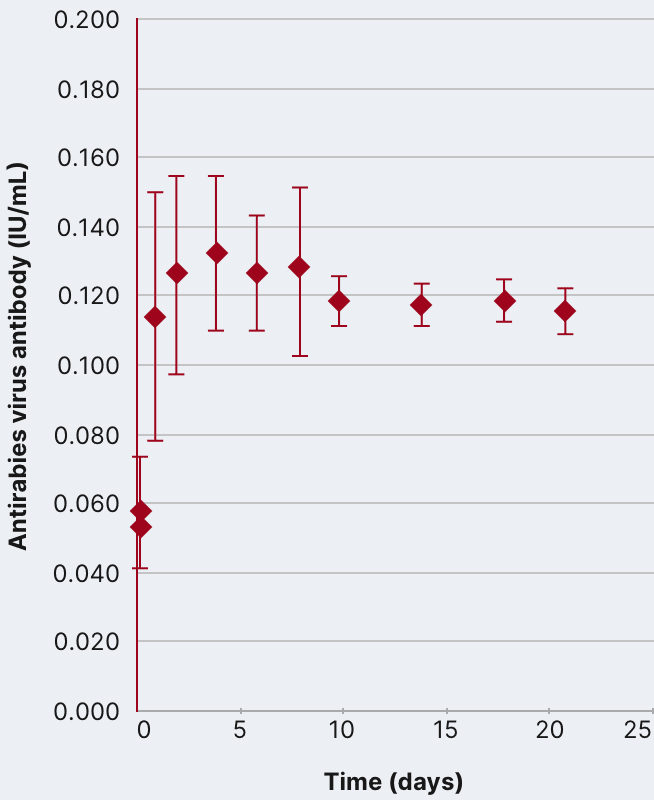
Data are presented as mean ± SD. Adapted from Hanna K et al. 2018.14
Importance of the antirabies virus antibody
HyperRAB provided interim protection until the host immune response to rabies vaccine produced definitive protective titers of neutralizing rabies antibody; therefore, the rabies vaccine series is also essential.1,14
Grifols has provided more than 45 years of consistent supply and product support.

HyperRAB is produced using a sophisticated caprylate/chromatography purification process that employs the highest quality and safety standards.
Main steps of the manufacturing process:

Caprylate precipitation

Depth filtration

Nanofiltration
Caprylate incubation

Low pH final container incubation
Column chromatography

The capacity of the HyperRAB manufacturing process to remove and/or inactivate viruses has been demonstrated by laboratory spiking studies on a scaled-down process model using a wide range of viruses with diverse physicochemical properties. This process provides the final product with a high margin of safety from the potential risk of transmission of infectious viruses.
The caprylate/chromatography manufacturing process was also investigated for its capacity to decrease the infectivity of an experimental agent of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE), considered as a model for the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agents. These studies provide reasonable assurance that low levels of vCJD/CJD agent infectivity, if present in the starting material, would be removed by the caprylate/chromatography manufacturing process.
HyperRAB is made from human blood and may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, eg, viruses, the vCJD agent, and, theoretically, the CJD agent.
Grifols employs a comprehensive tracking system called PediGri® that ensures full traceability from every donation.
For immediate, easy, and convenient access to all the information on the origin and quality of Grifols' plasma derivatives, visit www.pedigri.grifols.com.
HyperRAB CPT Code*
90375
Rabies immune globulin (RIG), human, for intramuscular use (150 IU)
Administration Procedures CPT Code*
96372
Therapeutic, prophylactic, or diagnostic injection (specify substance or drug); intramuscular
ICD-10-CM†
Z20.3
Contact with and (suspected) exposure to rabies
Z23
Encounter for immunization
Z29.14
Encounter for prophylactic rabies immune globin
A82.0
Sylvatic rabies
A82.1
Urban rabies
A82.9
Rabies, unspecified
W53.XXXX
Contact with rodent
W54.XXXX
Contact with dog
W55.XXXX
Contact with other mammals
HyperRAB NDC‡
13533-0318-01
1-mL vial 300 IU/mL (300 IU)
13533-0318-03
3-mL vial 300 IU/mL (900 IU)
13533-0318-05
5-mL vial 300 IU/mL (1500 IU)
| Coding System | Coding for HyperRAB | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
HyperRAB CPT Code* |
90375 |
Rabies immune globulin (RIG), human, for intramuscular use (150 IU) |
|
Administration Procedures CPT Code* |
96372 |
Therapeutic, prophylactic, or diagnostic injection (specify substance or drug); intramuscular |
|
ICD-10-CM† |
Z20.3 |
Contact with and (suspected) exposure to rabies |
|
Z23 |
Encounter for immunization |
|
|
Z29.14 |
Encounter for prophylactic rabies immune globin |
|
|
A82.0 |
Sylvatic rabies |
|
|
A82.1 |
Urban rabies |
|
|
A82.9 |
Rabies, unspecified |
|
|
W53.XXXX |
Contact with rodent |
|
|
W54.XXXX |
Contact with dog |
|
|
W55.XXXX |
Contact with other mammals |
|
|
HyperRAB NDC‡ |
13533-0318-01 |
1-mL vial 300 IU/mL (300 IU) |
|
13533-0318-03 |
3-mL vial 300 IU/mL (900 IU) |
|
|
13533-0318-05 |
5-mL vial 300 IU/mL (1500 IU) |
About Rabies
Gain a deeper understanding of rabies by exploring further information on this disease
Ordering Information
Interested in ordering HyperRAB? Find more information here
Resources
Discover documents and other helpful resources to help you and your patients understand rabies
Submit a request to get in contact with a representative.
Important Safety Information for HyperRAB® (rabies immune globulin [human])
Indication and Usage
HyperRAB® (rabies immune globulin [human]) is indicated for postexposure prophylaxis, along with rabies vaccine, for all persons suspected of exposure to rabies.
Limitations of Use
Persons who have been previously immunized with rabies vaccine and have a confirmed adequate rabies antibody titer should receive only vaccine.
For unvaccinated persons, the combination of HyperRAB and vaccine is recommended for both bite and nonbite exposures regardless of the time interval between exposure and initiation of postexposure prophylaxis.
Beyond 7 days (after the first vaccine dose), HyperRAB is not indicated since an antibody response to vaccine is presumed to have occurred.
Important Safety Information
For infiltration and intramuscular use only.
Severe hypersensitivity reactions may occur with HyperRAB. Patients with a history of prior systemic allergic reactions to human immunoglobulin preparations are at a greater risk of developing severe hypersensitivity and anaphylactic reactions. Have epinephrine available for treatment of acute allergic symptoms, should they occur.
HyperRAB is made from human blood and may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, eg, viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent, and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent.
The most common adverse reactions in >5% of subjects during clinical trials were injection-site pain, headache, injection-site nodule, abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence, nasal congestion, and oropharyngeal pain.
Do not administer repeated doses of HyperRAB once vaccine treatment has been initiated as this could prevent the full expression of active immunity expected from the rabies vaccine.
Other antibodies in the HyperRAB preparation may interfere with the response to live vaccines such as measles, mumps, polio, or rubella. Defer immunization with live vaccines for 4 months after HyperRAB administration.
Please see full Prescribing Information for HyperRAB.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
References